Computer data is essentially any information that is processed or stored by a computer. This can include text, numbers, images, audio, and video, formatted in a way that computers can understand and manipulate.
Data is the foundation of all computing systems; it is what computers use to perform tasks, make decisions, and provide insights.
Types of Data
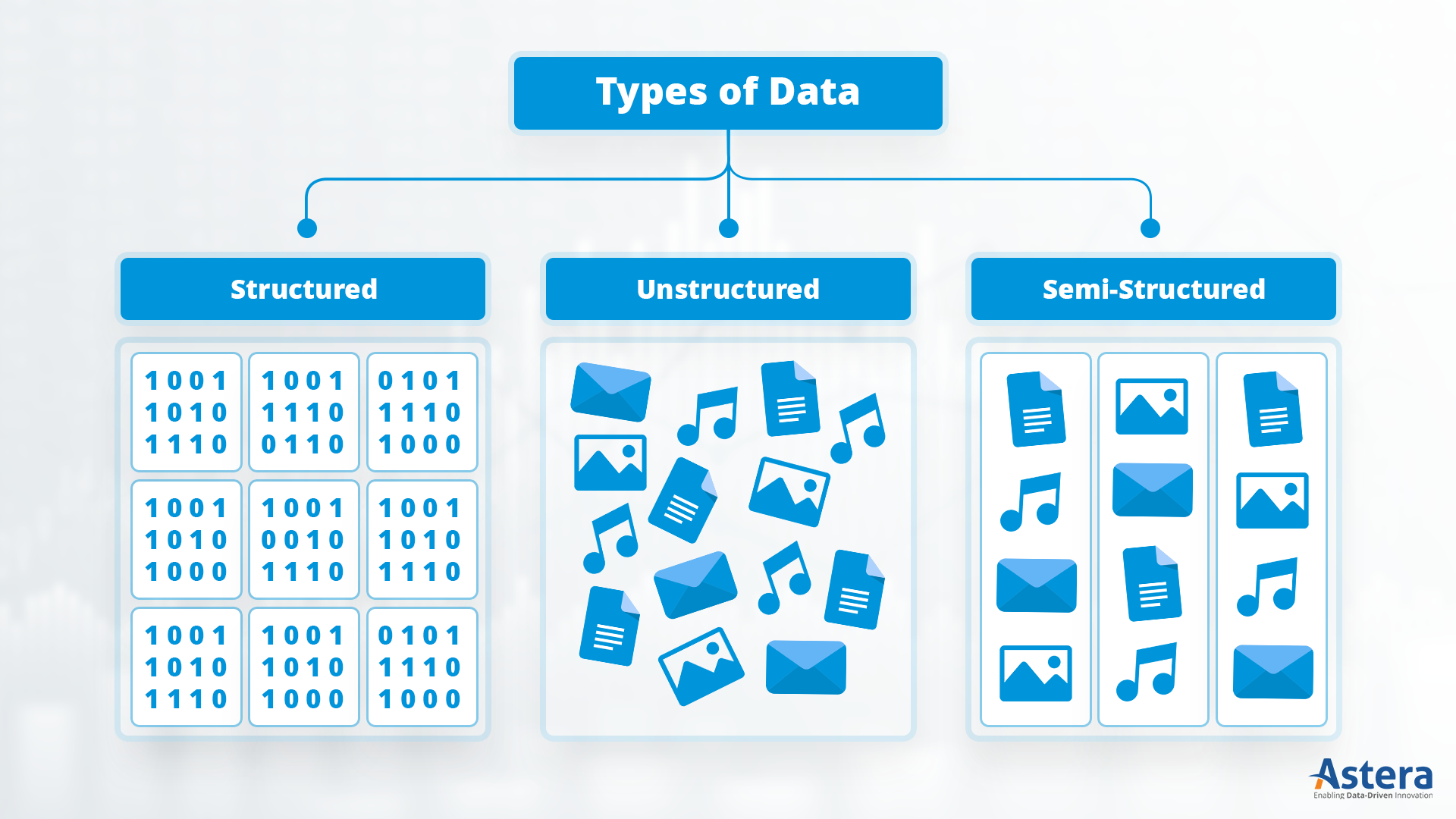
Data can be categorized in several ways:
-Structured Data: This type of data is organized in a defined manner, often in rows and columns, like databases or spreadsheets. Examples include customer records or financial transactions.
-Unstructured Data: This includes information that doesn’t have a predefined format, such as emails, social media posts, and multimedia files.
-Semi-structured Data: This type falls between structured and unstructured data. It has some organizational properties but does not fit neatly into a database. Examples include XML files and JSON.
The Evolution of Data Importance

Historically, data was collected primarily for record-keeping purposes. However, as technology advanced, the role of data transformed dramatically. The advent of computers allowed for faster processing and storage of vast amounts of information. Companies began to realize that data could be leveraged to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
In the digital age, the explosion of data has been unprecedented. According to estimates, we generate approximately 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day. This surge has been driven by the internet, social media, e-commerce, and IoT devices. As a result, data has become one of the most valuable assets for businesses.
Why Companies Are Pursuing Data
-Informed Decision-Making: Companies now rely heavily on data analytics to guide their strategic decisions. With access to real-time data insights, businesses can make informed choices that reduce risks and improve outcomes.
-Competitive Advantage: In today's market, having access to accurate and timely data can set a company apart from its competitors. Organizations that effectively utilize data can identify new opportunities for growth and innovation .
-Customer Understanding: Data allows companies to gain deeper insights into their customers' preferences and behaviors. By analyzing customer data, businesses can tailor their products and services to meet specific needs.
-Operational Efficiency: Data processing helps streamline operations by automating routine tasks and optimizing resource allocation. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces costs.
-Enhanced Marketing Strategies: Companies use data to refine their marketing efforts through targeted advertising and personalized customer experiences. By understanding what resonates with their audience, businesses can increase engagement and conversion rates.
The Role of Data Processing
Data processing refers to the collection and manipulation of data to produce meaningful information. It involves several stages:
-Input: Gathering raw data from various sources.
-Processing: Transforming the input into a more useful format through calculations or analysis.
-Output: Presenting the processed data in an understandable format, such as reports or visualizations.
This cycle is crucial for businesses as it enables them to turn raw data into actionable insights.
The Future of Data
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the importance of data. Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are making it easier for companies to analyze large datasets quickly and accurately. These advancements will further enhance the ability to predict trends and automate decision-making processes.
Moreover, with the increasing focus on privacy and security, organizations must also prioritize ethical data management practices. Ensuring that customer data is handled responsibly will be critical in maintaining trust and compliance with regulations.
Conclusion
In summary, computer data has become an indispensable part of modern life and business operations. Its evolution from simple record-keeping to a crucial asset for decision-making underscores its importance in today’s digital landscape. As companies continue to harness the power of data through advanced processing techniques and analytics tools, those who adapt will thrive in an increasingly competitive environment.
The relentless pursuit of data reflects its value as not just a resource but as a cornerstone for future innovations across industries. In this age where "data is the new oil," organizations must cultivate their ability to extract meaningful insights from vast amounts of information if they wish to succeed in the future
